Create a control plane project
Now that you have an Upbound account and the up CLI installed, you are ready to create a control plane.
In this quickstart, you will:
- Scaffold a control plane project
- Define your own resource abstraction and templatization
- See the changes immediately
This quickstart teaches how to use Crossplane to build workflows for templating resources and exposing them as simplified resource abstraction. If you just want to manage the lifecycle of resources in an external system through Crossplane and Kubernetes, read Manage external resources with providers
Prerequisites
This quickstart takes around 10 minutes to complete. You should be familiar with YAML or programming in Go, Python, or KCL.
Before beginning, make sure you have:
- The up CLI installed
- A Docker-compatible container runtime installed and running on your system
Podman users
If you're using Podman instead of Docker, set the DOCKER_HOST environment variable to the Podman socket before running up commands:
export DOCKER_HOST=unix:///run/user/$(id -u)/podman/podman.sock
Create a control plane project
Crossplane works by letting you define new resource types in Kubernetes that invoke function pipelines to template and generate other resources. Just like any other software project, a control plane project is a source-level representation of your control plane.
Create a control plane project on your machine by running the following command:
up project init --scratch getting-started
This scaffolds a new project in a folder called getting-started. Change your
current working directory to the project root folder:
cd getting-started
Deploy your control plane
In the root directory of your project, build and run your project by running the following:
up project run --local --ingress
This launches an instance of Upbound Crossplane on your machine, wrapped and deployed in a container. Upbound Crossplane comes bundled with a Web UI.
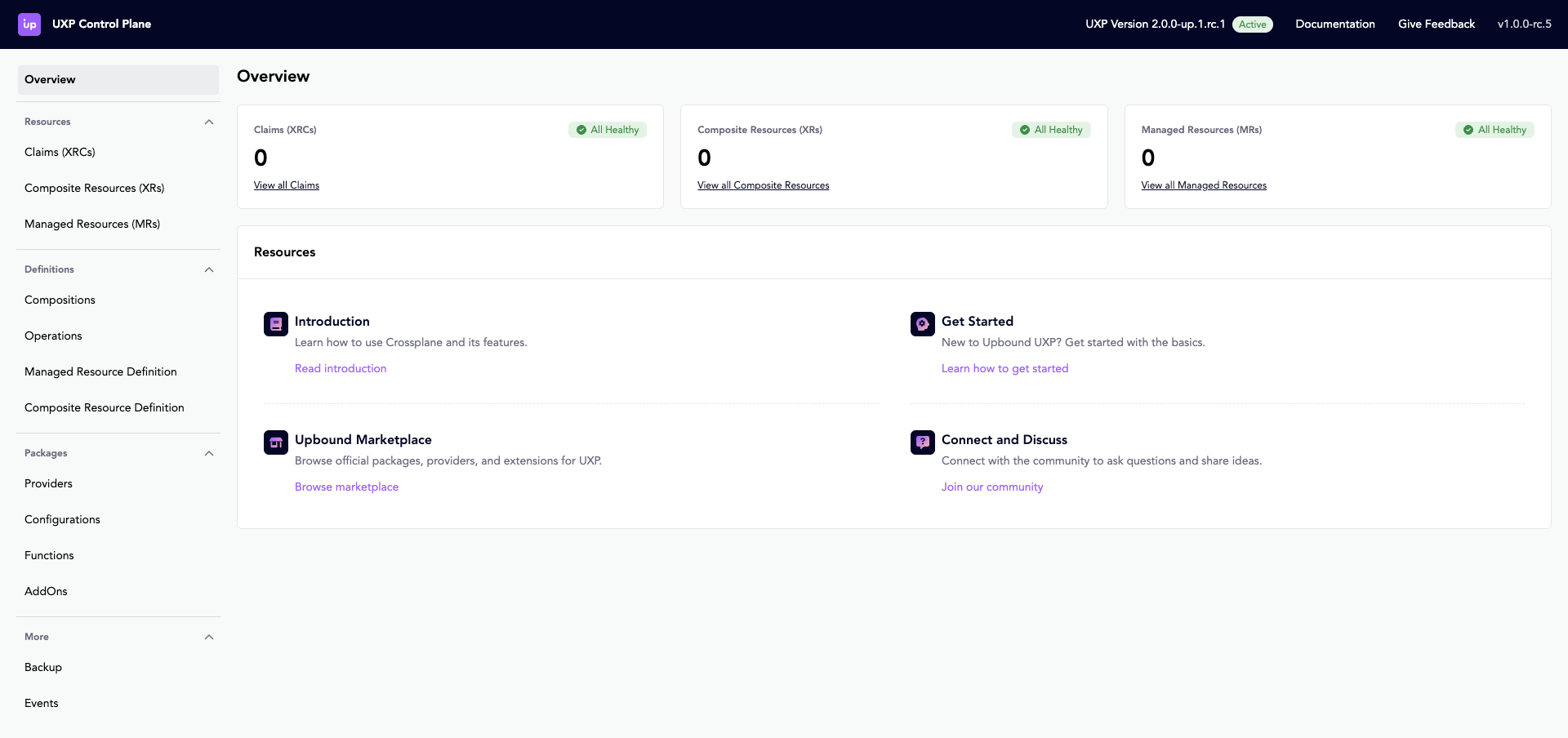
Define your own resource type
Customize your control plane by defining your own resource type.
Create an example instance of your custom resource type with:
up example generate \
--api-group platform.example.com \
--api-version v1alpha1 \
--kind WebApp\
--name my-app \
--scope namespace \
--namespace default
Open the project in your IDE of choice and replace the contents of the generated file
getting-started/examples/webapp/my-app.yaml with the following:
apiVersion: platform.example.com/v1alpha1
kind: WebApp
metadata:
name: my-app
namespace: default
spec:
parameters:
image: nginx
port: 8080
replicas: 1
service:
enabled: true
ingress:
enabled: false
serviceAccount: default
resources:
requests:
memory: "64Mi"
cpu: "250m"
limits:
memory: "1Gi"
cpu: "1"
status:
availableReplicas: 1
url: "http://localhost:8080"
Next, generate the definition files needed by Crossplane with the following commands:
- Go Templates
- Python
- Go
- KCL
up xrd generate examples/webapp/my-app.yaml
up composition generate apis/webapps/definition.yaml
up function generate --language=go-templating compose-resources apis/webapps/composition.yaml
up dependency add --api k8s:v1.33.0
up xrd generate examples/webapp/my-app.yaml
up composition generate apis/webapps/definition.yaml
up function generate --language=python compose-resources apis/webapps/composition.yaml
up dependency add --api k8s:v1.33.0
up xrd generate examples/webapp/my-app.yaml
up composition generate apis/webapps/definition.yaml
up function generate --language=go compose-resources apis/webapps/composition.yaml
up dependency add --api k8s:v1.33.0
up xrd generate examples/webapp/my-app.yaml
up composition generate apis/webapps/definition.yaml
up function generate --language=kcl compose-resources apis/webapps/composition.yaml
up dependency add --api k8s:v1.33.0
You just created your own resource type called WebApp. You generated a function
containing the logic Crossplane uses to determine what should happen when you
create the WebApp.
To define a new resource type with Crossplane, you need to:
- create a CompositeResourceDefinition (XRD), which defines the API schema of your resource type
- create a Composition, which defines the implementation of that API schema.
- A Composition is a pipeline of functions, which contain the user-defined logic of your composition.
Open the function definition file at
getting-started/functions/compose-resources/ and replace the contents with the
following:
- Go Templates
- Python
- Go
- KCL
# code: language=yaml
# yaml-language-server: $schema=../../.up/json/models/index.schema.json
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
annotations:
gotemplating.fn.crossplane.io/composition-resource-name: deployment
{{ if eq (.observed.resources.deployment | getResourceCondition "Available").Status "True" }}
gotemplating.fn.crossplane.io/ready: "True"
{{ end }}
name: {{ .observed.composite.resource.metadata.name }}
namespace: {{ .observed.composite.resource.metadata.namespace }}
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: {{ .observed.composite.resource.metadata.name }}
spec:
replicas: {{ .observed.composite.resource.spec.parameters.replicas }}
selector:
matchLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: {{ .observed.composite.resource.metadata.name }}
app: {{ .observed.composite.resource.metadata.name }}
strategy: {}
template:
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: {{ .observed.composite.resource.metadata.name }}
app: {{ .observed.composite.resource.metadata.name }}
spec:
serviceAccountName: {{ .observed.composite.resource.spec.parameters.serviceAccount }}
containers:
- name: {{ .observed.composite.resource.metadata.name }}
image: {{ .observed.composite.resource.spec.parameters.image }}
imagePullPolicy: Always
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: {{ .observed.composite.resource.spec.parameters.port }}
protocol: TCP
resources:
requests:
memory: {{ .observed.composite.resource.spec.parameters.resources.requests.memory }}
cpu: {{ .observed.composite.resource.spec.parameters.resources.requests.cpu }}
limits:
memory: {{ .observed.composite.resource.spec.parameters.resources.limits.memory }}
cpu: {{ .observed.composite.resource.spec.parameters.resources.limits.cpu }}
restartPolicy: Always
status: {}
{{ if .observed.composite.resource.spec.parameters.ingress.enabled }}
---
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
gotemplating.fn.crossplane.io/composition-resource-name: ingress
{{ if (get (getComposedResource . "ingress").status.loadBalancer.ingress 0).hostname }}
gotemplating.fn.crossplane.io/ready: "True"
{{ end }}
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: alb
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/scheme: internet-facing
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/target-type: ip
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-path: /health
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/listen-ports: '[{"HTTP": 80}]'
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/target-group-attributes: stickiness.enabled=true,stickiness.lb_cookie.duration_seconds=60
name: {{ .observed.composite.resource.metadata.name }}
namespace: {{ .observed.composite.resource.metadata.namespace }}
spec:
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: {{ .observed.composite.resource.metadata.name }}
port:
number: 80
{{ end }}
{{ if .observed.composite.resource.spec.parameters.service.enabled }}
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
annotations:
gotemplating.fn.crossplane.io/composition-resource-name: service
{{ if (get (getComposedResource . "service").spec "clusterIP") }}
gotemplating.fn.crossplane.io/ready: "True"
{{ end }}
name: {{ .observed.composite.resource.metadata.name }}
namespace: {{ .observed.composite.resource.metadata.namespace }}
spec:
selector:
app: {{ .observed.composite.resource.metadata.name }}
ports:
- name: http
protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: http
status:
loadBalancer: {}
{{ end }}
---
apiVersion: {{ .observed.composite.resource.apiVersion }}
kind: {{ .observed.composite.resource.kind }}
status:
{{ with $deployment := getComposedResource . "deployment" }}
availableReplicas: {{ $deployment.status.availableReplicas | default 0 }}
{{ else }}
availableReplicas: 0
{{ end }}
{{ with $ingress := getComposedResource . "ingress" }}
{{ with $hostname := (get $ingress.status.loadBalancer.ingress 0).hostname }}
url: {{ $hostname | quote }}
{{ else }}
url: ""
{{ end }}
{{ else }}
url: ""
{{ end }}
from crossplane.function import resource
from crossplane.function.proto.v1 import run_function_pb2 as fnv1
from .model.io.k8s.api.apps import v1 as appsv1
from .model.io.k8s.api.core import v1 as corev1
from .model.io.k8s.api.networking import v1 as networkingv1
from .model.com.example.platform.webapp import v1alpha1 as platformv1alpha1
from .model.io.k8s.apimachinery.pkg.apis.core.meta import v1 as coremetav1
def compose(req: fnv1.RunFunctionRequest, rsp: fnv1.RunFunctionResponse):
oxr = platformv1alpha1.WebApp(**req.observed.composite.resource)
ocds = req.observed.resources
# Create a Status object to collect updates
status = platformv1alpha1.Status()
deployment = appsv1.Deployment(
metadata=coremetav1.ObjectMeta(
name=oxr.metadata.name,
namespace=oxr.metadata.namespace,
labels={
"app.kubernetes.io/name": oxr.metadata.name
},
),
spec=appsv1.DeploymentSpec(
replicas=oxr.spec.parameters.replicas,
selector=coremetav1.LabelSelector(
matchLabels={
"app.kubernetes.io/name": oxr.metadata.name,
"app": oxr.metadata.name
}
),
template=corev1.PodTemplateSpec(
metadata=coremetav1.ObjectMeta(
labels={
"app.kubernetes.io/name": oxr.metadata.name,
"app": oxr.metadata.name
}
),
spec=corev1.PodSpec(
serviceAccountName=oxr.spec.parameters.serviceAccount,
containers=[
corev1.Container(
name=oxr.metadata.name,
image=oxr.spec.parameters.image,
imagePullPolicy="Always",
ports=[
corev1.ContainerPort(
name="http",
containerPort=int(oxr.spec.parameters.port),
protocol="TCP",
)
],
resources=corev1.ResourceRequirements(
requests={
"memory": oxr.spec.parameters.resources.requests.memory,
"cpu": oxr.spec.parameters.resources.requests.cpu
},
limits={
"memory": oxr.spec.parameters.resources.limits.memory,
"cpu": oxr.spec.parameters.resources.limits.cpu
}
)
)
],
restartPolicy="Always"
)
)
)
)
if "deployment" in ocds:
observed_deployment = appsv1.Deployment(**ocds["deployment"].resource)
if observed_deployment.status and observed_deployment.status.conditions:
for condition in observed_deployment.status.conditions:
if condition.type == "Available" and condition.status == "True":
rsp.desired.resources["deployment"].ready = True
break
resource.update(rsp.desired.resources["deployment"], deployment)
if oxr.spec.parameters.service and oxr.spec.parameters.service.enabled:
service = corev1.Service(
metadata=coremetav1.ObjectMeta(
name=oxr.metadata.name,
namespace=oxr.metadata.namespace,
),
spec=corev1.ServiceSpec(
selector={
"app": oxr.metadata.name
},
ports=[
corev1.ServicePort(
name="http",
protocol="TCP",
port=80,
targetPort="http"
)
]
)
)
if "service" in ocds:
observed_service = corev1.Service(**ocds["service"].resource)
if observed_service.spec and observed_service.spec.clusterIP:
rsp.desired.resources["service"].ready = True
resource.update(rsp.desired.resources["service"], service)
if oxr.spec.parameters.ingress and oxr.spec.parameters.ingress.enabled:
ingress = networkingv1.Ingress(
metadata=coremetav1.ObjectMeta(
name=oxr.metadata.name,
namespace=oxr.metadata.namespace,
annotations={
"kubernetes.io/ingress.class": "alb",
"alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/scheme": "internet-facing",
"alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/target-type": "ip",
"alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-path": "/health",
"alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/listen-ports": '[{"HTTP": 80}]',
"alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/target-group-attributes": "stickiness.enabled=true,stickiness.lb_cookie.duration_seconds=60"
}
),
spec=networkingv1.IngressSpec(
rules=[
networkingv1.IngressRule(
http=networkingv1.HTTPIngressRuleValue(
paths=[
networkingv1.HTTPIngressPath(
path="/",
pathType="Prefix",
backend=networkingv1.IngressBackend(
service=networkingv1.IngressServiceBackend(
name=oxr.metadata.name,
port=networkingv1.ServiceBackendPort(
number=80
)
)
)
)
]
)
)
]
)
)
if "ingress" in ocds:
observed_ingress = networkingv1.Ingress(**ocds["ingress"].resource)
if (observed_ingress.status and
observed_ingress.status.loadBalancer and
observed_ingress.status.loadBalancer.ingress and
len(observed_ingress.status.loadBalancer.ingress) > 0 and
observed_ingress.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].hostname):
rsp.desired.resources["ingress"].ready = True
resource.update(rsp.desired.resources["ingress"], ingress)
# Set status with defaults
if "deployment" in ocds:
observed_deployment = appsv1.Deployment(**ocds["deployment"].resource)
status.availableReplicas = observed_deployment.status.availableReplicas if observed_deployment.status and observed_deployment.status.availableReplicas else 0
else:
status.availableReplicas = 0
if "ingress" in ocds:
observed_ingress = networkingv1.Ingress(**ocds["ingress"].resource)
status.url = (
observed_ingress.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].hostname
if (observed_ingress.status and
observed_ingress.status.loadBalancer and
observed_ingress.status.loadBalancer.ingress and
len(observed_ingress.status.loadBalancer.ingress) > 0 and
observed_ingress.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].hostname)
else ""
)
else:
status.url = ""
resource.update(rsp.desired.composite, {"status": status.model_dump(exclude_none=True)})
package main
import (
"context"
"encoding/json"
"dev.upbound.io/models/com/example/platform/v1alpha1"
appsv1 "dev.upbound.io/models/io/k8s/apps/v1"
coremetav1 "dev.upbound.io/models/io/k8s/core/meta/v1"
corev1 "dev.upbound.io/models/io/k8s/core/v1"
networkingv1 "dev.upbound.io/models/io/k8s/networking/v1"
resourcev1 "dev.upbound.io/models/io/k8s/resource/v1"
"github.com/crossplane/crossplane-runtime/pkg/logging"
"github.com/crossplane/function-sdk-go/errors"
fnv1 "github.com/crossplane/function-sdk-go/proto/v1"
"github.com/crossplane/function-sdk-go/request"
"github.com/crossplane/function-sdk-go/resource"
"github.com/crossplane/function-sdk-go/resource/composed"
"github.com/crossplane/function-sdk-go/response"
"k8s.io/utils/ptr"
)
// Function is your composition function.
type Function struct {
fnv1.UnimplementedFunctionRunnerServiceServer
log logging.Logger
}
// RunFunction runs the Function.
func (f *Function) RunFunction(_ context.Context, req *fnv1.RunFunctionRequest) (*fnv1.RunFunctionResponse, error) {
f.log.Info("Running function", "tag", req.GetMeta().GetTag())
rsp := response.To(req, response.DefaultTTL)
observedComposite, err := request.GetObservedCompositeResource(req)
if err != nil {
response.Fatal(rsp, errors.Wrap(err, "cannot get xr"))
return rsp, nil
}
observedComposed, err := request.GetObservedComposedResources(req)
if err != nil {
response.Fatal(rsp, errors.Wrap(err, "cannot get observed resources"))
return rsp, nil
}
var xr v1alpha1.WebApp
if err := convertViaJSON(&xr, observedComposite.Resource); err != nil {
response.Fatal(rsp, errors.Wrap(err, "cannot convert xr"))
return rsp, nil
}
params := xr.Spec.Parameters
if params == nil {
response.Fatal(rsp, errors.New("missing parameters"))
return rsp, nil
}
// We'll collect our desired composed resources into this map, then convert
// them to the SDK's types and set them in the response when we return.
desiredComposed := make(map[resource.Name]any)
defer func() {
desiredComposedResources, err := request.GetDesiredComposedResources(req)
if err != nil {
response.Fatal(rsp, errors.Wrap(err, "cannot get desired resources"))
return
}
for name, obj := range desiredComposed {
c := composed.New()
if err := convertViaJSON(c, obj); err != nil {
response.Fatal(rsp, errors.Wrapf(err, "cannot convert %s to unstructured", name))
return
}
dc := &resource.DesiredComposed{Resource: c}
// Check if this resource should be marked as ready
if c.GetAnnotations()["go.upbound.io/ready"] == "True" {
dc.Ready = resource.ReadyTrue
}
desiredComposedResources[name] = dc
}
if err := response.SetDesiredComposedResources(rsp, desiredComposedResources); err != nil {
response.Fatal(rsp, errors.Wrap(err, "cannot set desired resources"))
return
}
}()
// Create Deployment
deployment := &appsv1.Deployment{
APIVersion: ptr.To(appsv1.DeploymentAPIVersionAppsV1),
Kind: ptr.To(appsv1.DeploymentKindDeployment),
Metadata: &coremetav1.ObjectMeta{
Name: xr.Metadata.Name,
Namespace: xr.Metadata.Namespace,
Labels: &map[string]string{
"app.kubernetes.io/name": *xr.Metadata.Name,
},
},
Spec: &appsv1.DeploymentSpec{
Replicas: ptr.To(int32(*params.Replicas)),
Selector: &coremetav1.LabelSelector{
MatchLabels: &map[string]string{
"app.kubernetes.io/name": *xr.Metadata.Name,
"app": *xr.Metadata.Name,
},
},
// ToDo(haarchri): remove this
Strategy: &appsv1.IoK8SApiAppsV1DeploymentStrategy{},
Template: &corev1.PodTemplateSpec{
Metadata: &coremetav1.ObjectMeta{
Labels: &map[string]string{
"app.kubernetes.io/name": *xr.Metadata.Name,
"app": *xr.Metadata.Name,
},
},
Spec: &corev1.PodSpec{
ServiceAccountName: params.ServiceAccount,
Containers: &[]corev1.Container{{
Name: xr.Metadata.Name,
Image: params.Image,
ImagePullPolicy: ptr.To("Always"),
Ports: &[]corev1.ContainerPort{{
Name: ptr.To("http"),
ContainerPort: ptr.To(int32(*params.Port)),
Protocol: ptr.To("TCP"),
}},
Resources: &corev1.ResourceRequirements{
Requests: &map[string]resourcev1.Quantity{
"memory": *params.Resources.Requests.Memory,
"cpu": *params.Resources.Requests.CPU,
},
Limits: &map[string]resourcev1.Quantity{
"memory": *params.Resources.Limits.Memory,
"cpu": *params.Resources.Limits.CPU,
},
},
}},
RestartPolicy: ptr.To("Always"),
},
},
},
// ToDo(haarchri): remove this
Status: &appsv1.IoK8SApiAppsV1DeploymentStatus{},
}
// Check if deployment is ready
observedDeployment, ok := observedComposed["deployment"]
if ok && observedDeployment.Resource != nil {
var obsDeployment appsv1.Deployment
if err := convertViaJSON(&obsDeployment, observedDeployment.Resource); err == nil {
if obsDeployment.Status != nil && obsDeployment.Status.Conditions != nil {
for _, c := range *obsDeployment.Status.Conditions {
if c.Type != nil && *c.Type == "Available" &&
c.Status != nil && *c.Status == "True" {
if deployment.Metadata.Annotations == nil {
deployment.Metadata.Annotations = &map[string]string{}
}
(*deployment.Metadata.Annotations)["go.upbound.io/ready"] = "True"
break
}
}
}
}
}
desiredComposed["deployment"] = deployment
// Create Service if enabled
if params.Service != nil && params.Service.Enabled != nil && *params.Service.Enabled {
service := &corev1.Service{
APIVersion: ptr.To(corev1.ServiceAPIVersionV1),
Kind: ptr.To(corev1.ServiceKindService),
Metadata: &coremetav1.ObjectMeta{
Name: xr.Metadata.Name,
Namespace: xr.Metadata.Namespace,
},
Spec: &corev1.ServiceSpec{
Selector: &map[string]string{
"app": *xr.Metadata.Name,
},
Ports: &[]corev1.ServicePort{{
Name: ptr.To("http"),
Protocol: ptr.To("TCP"),
Port: ptr.To(int32(80)),
TargetPort: ptr.To("http"),
}},
},
// ToDo(haarchri): remove this
Status: &corev1.ServiceStatus{
LoadBalancer: &corev1.LoadBalancerStatus{},
},
}
// Check if service is ready
observedService, ok := observedComposed["service"]
if ok && observedService.Resource != nil {
var obsService corev1.Service
if err := convertViaJSON(&obsService, observedService.Resource); err == nil {
if obsService.Spec != nil && obsService.Spec.ClusterIP != nil && *obsService.Spec.ClusterIP != "" {
if service.Metadata.Annotations == nil {
service.Metadata.Annotations = &map[string]string{}
}
(*service.Metadata.Annotations)["go.upbound.io/ready"] = "True"
}
}
}
desiredComposed["service"] = service
}
// Create Ingress if enabled
if params.Ingress != nil && params.Ingress.Enabled != nil && *params.Ingress.Enabled {
ingress := &networkingv1.Ingress{
APIVersion: ptr.To(networkingv1.IngressAPIVersionNetworkingK8SIoV1),
Kind: ptr.To(networkingv1.IngressKindIngress),
Metadata: &coremetav1.ObjectMeta{
Name: xr.Metadata.Name,
Namespace: xr.Metadata.Namespace,
Annotations: &map[string]string{
"kubernetes.io/ingress.class": "alb",
"alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/scheme": "internet-facing",
"alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/target-type": "ip",
"alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-path": "/health",
"alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/listen-ports": `[{"HTTP": 80}]`,
"alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/target-group-attributes": "stickiness.enabled=true,stickiness.lb_cookie.duration_seconds=60",
},
},
Spec: &networkingv1.IngressSpec{
Rules: &[]networkingv1.IngressRule{{
HTTP: &networkingv1.HTTPIngressRuleValue{
Paths: &[]networkingv1.HTTPIngressPath{{
Path: ptr.To("/"),
PathType: ptr.To("Prefix"),
Backend: &networkingv1.IngressBackend{
Service: &networkingv1.IngressServiceBackend{
Name: xr.Metadata.Name,
Port: &networkingv1.ServiceBackendPort{
Number: ptr.To(int32(80)),
},
},
},
}},
},
}},
},
}
// Check if ingress is ready
observedIngress, ok := observedComposed["ingress"]
if ok && observedIngress.Resource != nil {
var obsIngress networkingv1.Ingress
if err := convertViaJSON(&obsIngress, observedIngress.Resource); err == nil {
if obsIngress.Status != nil && obsIngress.Status.LoadBalancer != nil &&
obsIngress.Status.LoadBalancer.Ingress != nil && len(*obsIngress.Status.LoadBalancer.Ingress) > 0 {
firstIngress := (*obsIngress.Status.LoadBalancer.Ingress)[0]
if firstIngress.Hostname != nil && *firstIngress.Hostname != "" {
if ingress.Metadata.Annotations == nil {
ingress.Metadata.Annotations = &map[string]string{}
}
(*ingress.Metadata.Annotations)["go.upbound.io/ready"] = "True"
}
}
}
}
desiredComposed["ingress"] = ingress
}
// Update XR status
desiredXR, err := request.GetDesiredCompositeResource(req)
if err != nil {
response.Fatal(rsp, errors.Wrap(err, "cannot get desired composite resource"))
return rsp, nil
}
// Convert desired XR to WebApp
var desiredWebApp v1alpha1.WebApp
desiredWebApp.APIVersion = ptr.To(v1alpha1.WebAppAPIVersionplatformExampleComV1Alpha1)
desiredWebApp.Kind = ptr.To(v1alpha1.WebAppKindWebApp)
if err := convertViaJSON(&desiredWebApp, desiredXR.Resource); err != nil {
response.Fatal(rsp, errors.Wrap(err, "cannot convert desired xr"))
return rsp, nil
}
// Update status fields
if desiredWebApp.Status == nil {
desiredWebApp.Status = &v1alpha1.WebAppStatus{}
}
// Set deployment conditions
if observedDeployment, ok := observedComposed["deployment"]; ok && observedDeployment.Resource != nil {
var obsDeployment appsv1.Deployment
if err := convertViaJSON(&obsDeployment, observedDeployment.Resource); err == nil {
if obsDeployment.Status != nil {
if obsDeployment.Status.AvailableReplicas != nil {
desiredWebApp.Status.AvailableReplicas = ptr.To(float32(*obsDeployment.Status.AvailableReplicas))
} else {
// Set default value when no available replicas
desiredWebApp.Status.AvailableReplicas = ptr.To(float32(0))
}
} else {
// Set defaults when status is nil
desiredWebApp.Status.AvailableReplicas = ptr.To(float32(0))
}
}
} else {
// Set defaults when deployment doesn't exist
desiredWebApp.Status.AvailableReplicas = ptr.To(float32(0))
}
// Set ingress URL
if observedIngress, ok := observedComposed["ingress"]; ok && observedIngress.Resource != nil {
var obsIngress networkingv1.Ingress
if err := convertViaJSON(&obsIngress, observedIngress.Resource); err == nil {
if obsIngress.Status != nil && obsIngress.Status.LoadBalancer != nil &&
obsIngress.Status.LoadBalancer.Ingress != nil && len(*obsIngress.Status.LoadBalancer.Ingress) > 0 {
firstIngress := (*obsIngress.Status.LoadBalancer.Ingress)[0]
if firstIngress.Hostname != nil {
desiredWebApp.Status.URL = firstIngress.Hostname
} else {
// Set empty string when hostname is nil
desiredWebApp.Status.URL = ptr.To("")
}
} else {
// Set empty string when no load balancer ingress
desiredWebApp.Status.URL = ptr.To("")
}
} else {
// Set empty string when conversion fails
desiredWebApp.Status.URL = ptr.To("")
}
} else {
// Set empty string when ingress doesn't exist
desiredWebApp.Status.URL = ptr.To("")
}
// Convert back to unstructured
if err := convertViaJSON(desiredXR.Resource, &desiredWebApp); err != nil {
response.Fatal(rsp, errors.Wrap(err, "cannot convert desired webapp back to unstructured"))
return rsp, nil
}
if err := response.SetDesiredCompositeResource(rsp, desiredXR); err != nil {
response.Fatal(rsp, errors.Wrap(err, "cannot set desired composite resource"))
return rsp, nil
}
return rsp, nil
}
func convertViaJSON(to, from any) error {
bs, err := json.Marshal(from)
if err != nil {
return err
}
return json.Unmarshal(bs, to)
}
import models.io.k8s.api.apps.v1 as appsv1
import models.io.k8s.api.core.v1 as corev1
import models.io.k8s.api.networking.v1 as networkingv1
import models.com.example.platform.v1alpha1 as platformv1alpha1
oxr = platformv1alpha1.WebApp{**option("params").oxr} # observed claim
_ocds = option("params").ocds # observed composed resources
_dxr = option("params").dxr # desired composite resource
dcds = option("params").dcds # desired composed resources
_metadata = lambda name: str -> any {
{ annotations = { "krm.kcl.dev/composition-resource-name" = name }}
}
_desired_deployment = appsv1.Deployment{
metadata: _metadata("deployment") | {
name: oxr.metadata.name
namespace: oxr.metadata.namespace
labels: {
"app.kubernetes.io/name": oxr.metadata.name
}
}
spec: {
replicas: int(oxr.spec.parameters.replicas)
selector: {
matchLabels: {
"app.kubernetes.io/name": oxr.metadata.name
app: oxr.metadata.name
}
}
template: {
metadata: {
labels: {
"app.kubernetes.io/name": oxr.metadata.name
app: oxr.metadata.name
}
}
spec: {
serviceAccountName: oxr.spec.parameters.serviceAccount
containers: [{
name: oxr.metadata.name
image: oxr.spec.parameters.image
imagePullPolicy: "Always"
ports: [{
name: "http"
containerPort: int(oxr.spec.parameters.port)
protocol: "TCP"
}]
resources: {
requests: {
memory: oxr.spec.parameters.resources.requests.memory
cpu: oxr.spec.parameters.resources.requests.cpu
}
limits: {
memory: oxr.spec.parameters.resources.limits.memory
cpu: oxr.spec.parameters.resources.limits.cpu
}
}
}]
restartPolicy: "Always"
}
}
}
}
observed_deployment = option("params").ocds["deployment"]?.Resource
if any_true([c.type == "Available" and c.status == "True" for c in observed_deployment?.status?.conditions or []]):
_desired_deployment.metadata.annotations["krm.kcl.dev/ready"] = "True"
if oxr.spec.parameters.service.enabled:
_desired_service = corev1.Service{
metadata: _metadata("service") | {
name: oxr.metadata.name
namespace: oxr.metadata.namespace
}
spec: {
selector: {
app: oxr.metadata.name
}
ports: [{
name: "http"
protocol: "TCP"
port: 80
targetPort: "http"
}]
}
}
observed_service = option("params").ocds["service"]?.Resource
if observed_service?.spec?.clusterIP:
_desired_service.metadata.annotations["krm.kcl.dev/ready"] = "True"
if oxr.spec.parameters.ingress.enabled:
_desired_ingress = networkingv1.Ingress{
metadata: _metadata("ingress") | {
name: oxr.metadata.name
namespace: oxr.metadata.namespace
annotations: {
"kubernetes.io/ingress.class": "alb"
"alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/scheme": "internet-facing"
"alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/target-type": "ip"
"alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/healthcheck-path": "/health"
"alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/listen-ports": '[{"HTTP": 80}]'
"alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/target-group-attributes": "stickiness.enabled=true,stickiness.lb_cookie.duration_seconds=60"
}
}
spec: {
rules: [{
http: {
paths: [{
path: "/"
pathType: "Prefix"
backend: {
service: {
name: oxr.metadata.name
port: {
number: 80
}
}
}
}]
}
}]
}
}
observed_ingress = option("params").ocds["ingress"]?.Resource
if observed_ingress?.status?.loadBalancer?.ingress?[0]?.hostname:
_desired_ingress.metadata.annotations["krm.kcl.dev/ready"] = "True"
_desired_xr = {
**option("params").dxr
status.availableReplicas = observed_deployment?.status?.availableReplicas or 0
status.url = observed_ingress?.status?.loadBalancer?.ingress?[0]?.hostname or ""
}
items = [
_desired_deployment,
_desired_service,
_desired_ingress,
_desired_xr
]
Deploy the changes you made to your control plane:
up project run --local --ingress
The project run command builds and deploys any changes. If you don't have a control plane running yet, it creates one, otherwise it'll target your existing control plane.
Use the custom resource
Your control plane now understands WebApp resources. Create a WebApp:
kubectl apply -f examples/webapp/my-app.yaml
Check that the WebApp is ready:
kubectl get -f examples/webapp/my-app.yaml
NAME SYNCED READY COMPOSITION AGE
my-app True True app-yaml 56s
Observe the Deployment and Service Crossplane created when you created the WebApp:
kubectl get deploy,service -l crossplane.io/composite=my-app
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/my-app-2r2rk 2/2 2 2 11m
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/my-app-xfkzg ClusterIP 10.96.148.56 <none> 8080/TCP 11m
Next steps
Now that you know the basics of building with Upbound, extend your WebApp custom resource type with an AI-augmented operation to detect and remediate issues that occur when running app workloads on Kubernetes. Read Create an AI-augmented operation.